Cube
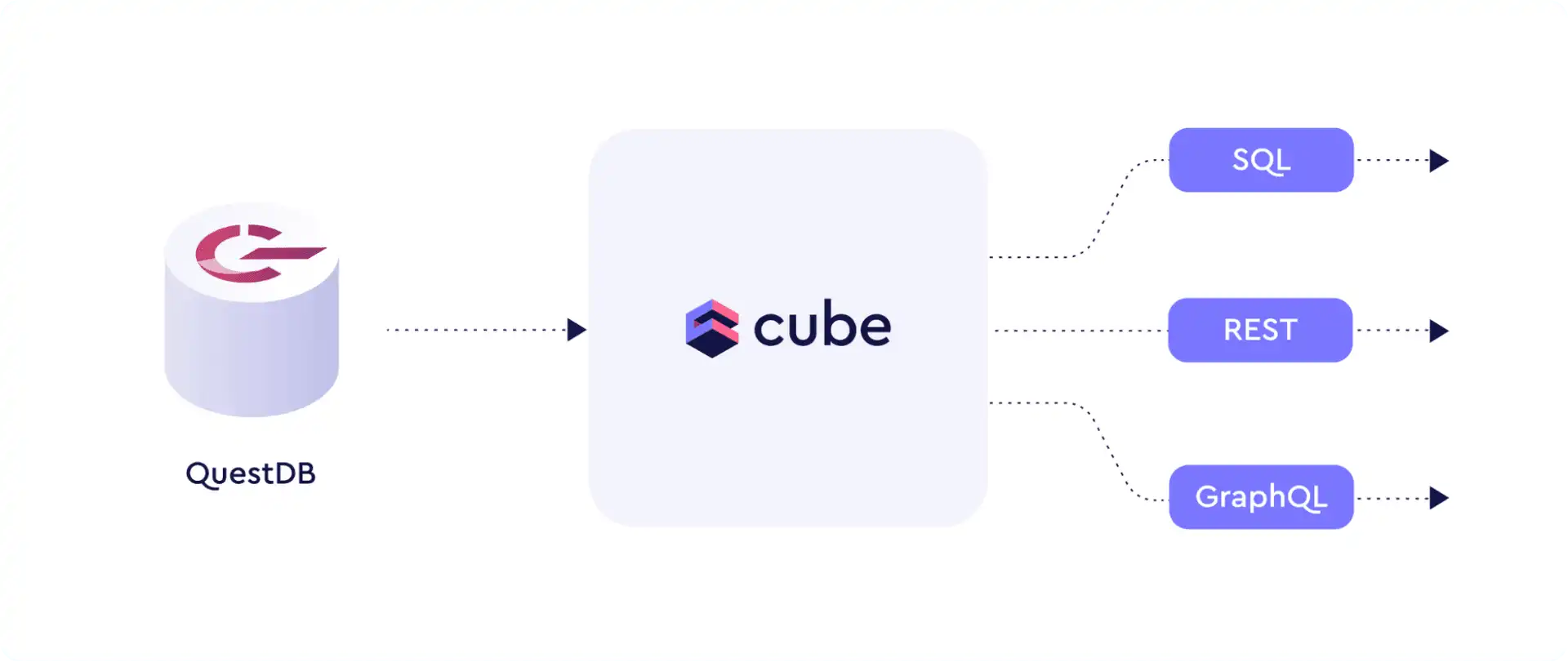
Cube is middleware that connects your data sources and your data applications. Cube provides an API-first semantic layer for consolidating, caching, and securing connections. Instead of having independent lines between data stores and analytics, business or AI tools, Cube consolidates the complexity of overall data modelling and cross-source data exchange into a cleaner interface.
As a high performance time-series database, QuestDB and Cube are a strong pair. Together, they efficiently bridge your QuestDB data to one of the many applications and libraries which integrate with Cube.
Getting Started
This section will help you get QuestDB and Cube running together using Docker.
Prerequisites
Setup
Create a project directory:
mkdir questdb-cube && cd $_
Create a docker-compose.yml file:
version: "2.2"
services:
cube:
environment:
- CUBEJS_DEV_MODE=true
image: "cubejs/cube:latest"
ports:
- "4000:4000"
env_file: "cube.env"
volumes:
- ".:/cube/conf"
questdb:
container_name: questdb
hostname: questdb
image: "questdb/questdb:latest"
ports:
- "9000:9000"
- "8812:8812"
Create a cube.env file with connection details:
CUBEJS_DB_HOST=questdb
CUBEJS_DB_PORT=8812
CUBEJS_DB_NAME=qdb
CUBEJS_DB_USER=admin
CUBEJS_DB_PASS=quest
CUBEJS_DB_TYPE=questdb
Create a model directory for Cube and start the containers:
mkdir model
docker-compose up -d
Both applications are now available:
- QuestDB Web Console:
http://localhost:9000 - Cube Playground:
http://localhost:4000
Tutorial: Crypto Price Analytics
In this tutorial, we'll build a crypto price analysis pipeline using the Kaggle Crypto dataset (requires a free Kaggle account to download). We'll import data into QuestDB, build a Cube data model, and expose it via APIs.
Importing Data into QuestDB
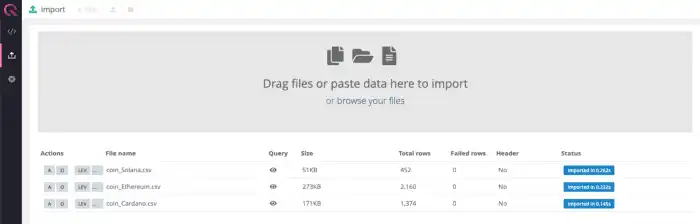
Navigate to http://localhost:9000 to open QuestDB's Web Console. Click on the
"Upload" icon on the left-hand panel, and import a
CSV file from the Kaggle dataset.
This example uses the Ethereum dataset, but any coin dataset will work.
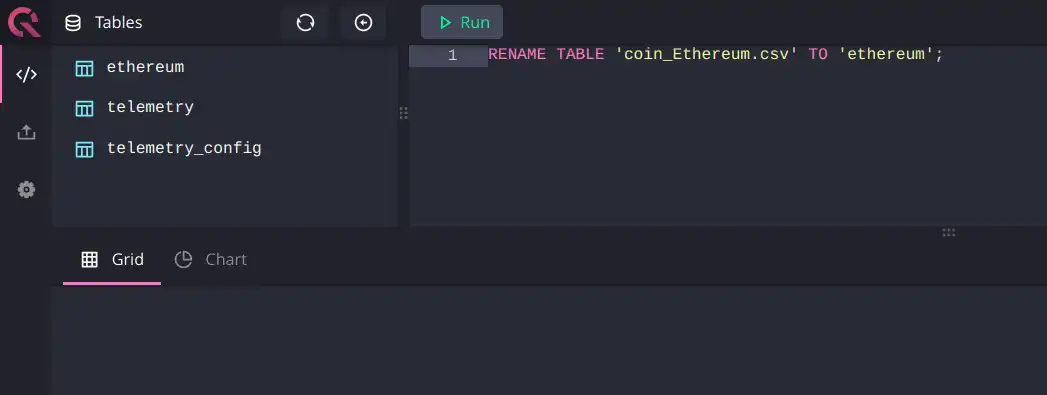
Cube works best with table names that do not contain special characters. Rename the table:
RENAME TABLE 'coin_Ethereum.csv' TO 'ethereum';
You can now query the data:
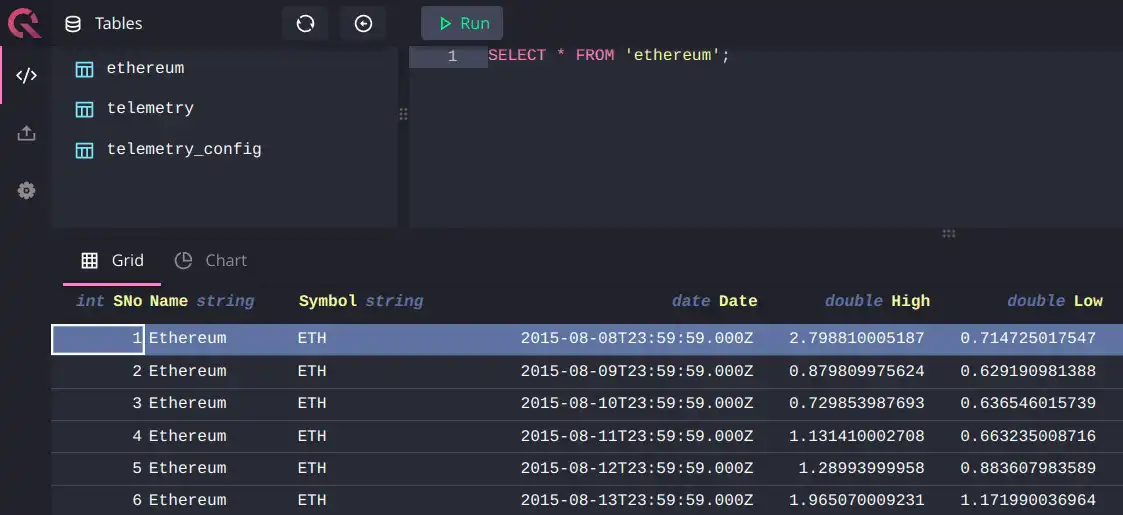
Building a Cube Data Model
The Cube data model consists of entities called 'cubes' that define metrics by dimensions (qualitative categories) and measures (numerical values).
Navigate to http://localhost:4000/#/schema and select the ethereum table:
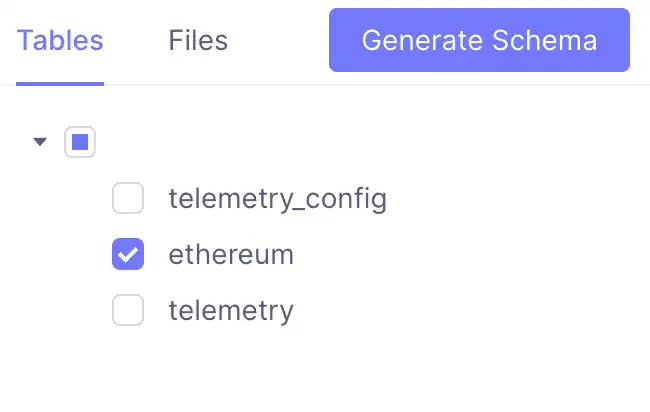
Click "Generate Data Model" to create a cube in the model directory. Open the
generated Ethereum.js file and customize it to include price columns:
cube(`Ethereum`, {
sql: `SELECT * FROM ethereum`,
measures: {
count: {
type: `count`,
drillMembers: [name, date],
},
avgHigh: {
type: "avg",
sql: `${CUBE}."High"`,
},
avgLow: {
type: "avg",
sql: `${CUBE}."Low"`,
},
},
dimensions: {
name: {
sql: `${CUBE}."Name"`,
type: `string`,
},
symbol: {
sql: `${CUBE}."Symbol"`,
type: `string`,
},
date: {
sql: `${CUBE}."Date"`,
type: `time`,
},
high: {
type: "number",
sql: `${CUBE}."High"`,
},
low: {
type: "number",
sql: `${CUBE}."Low"`,
},
},
})
In the Cube Playground "Build" tab, you can now query and visualize the data:
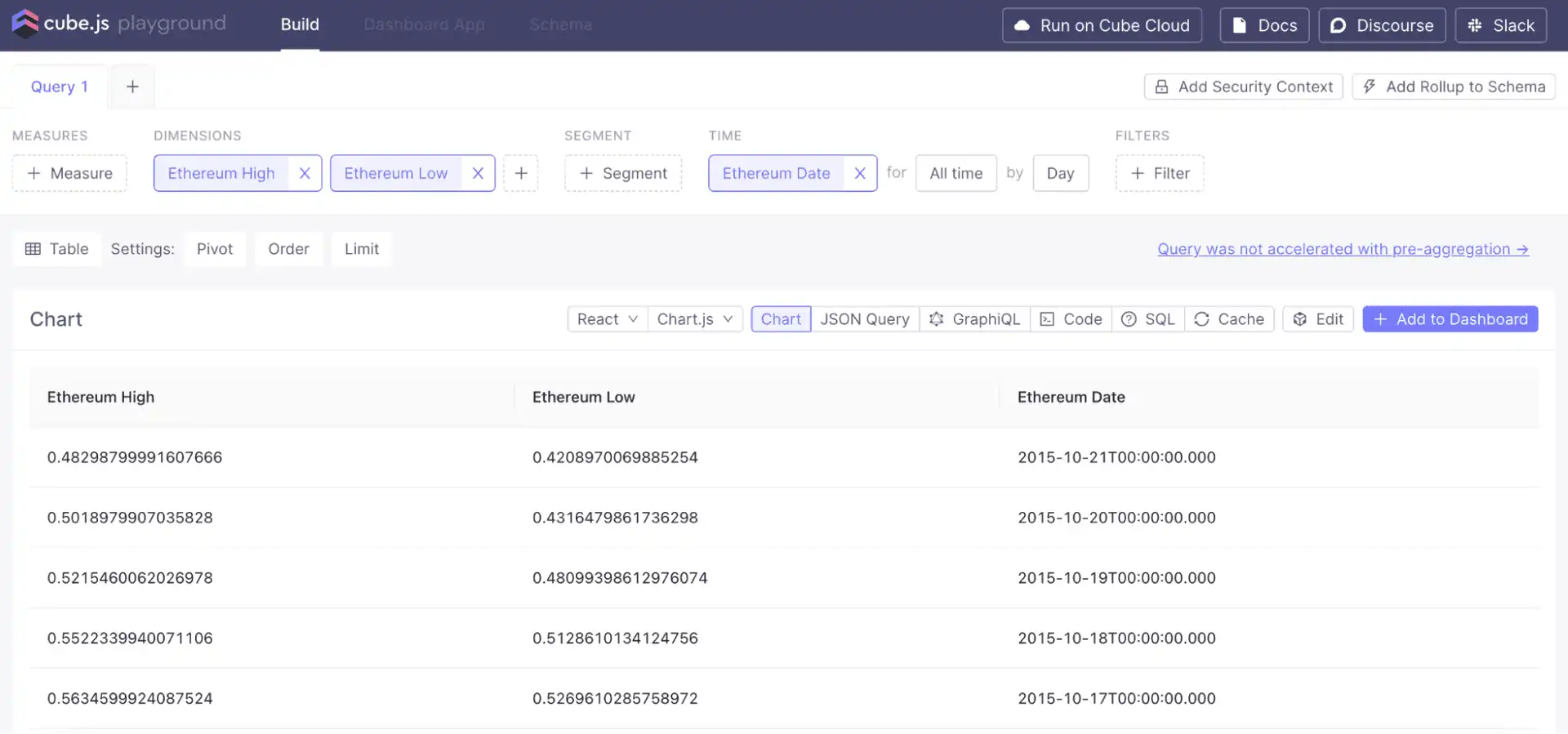
Create a price-over-time chart:
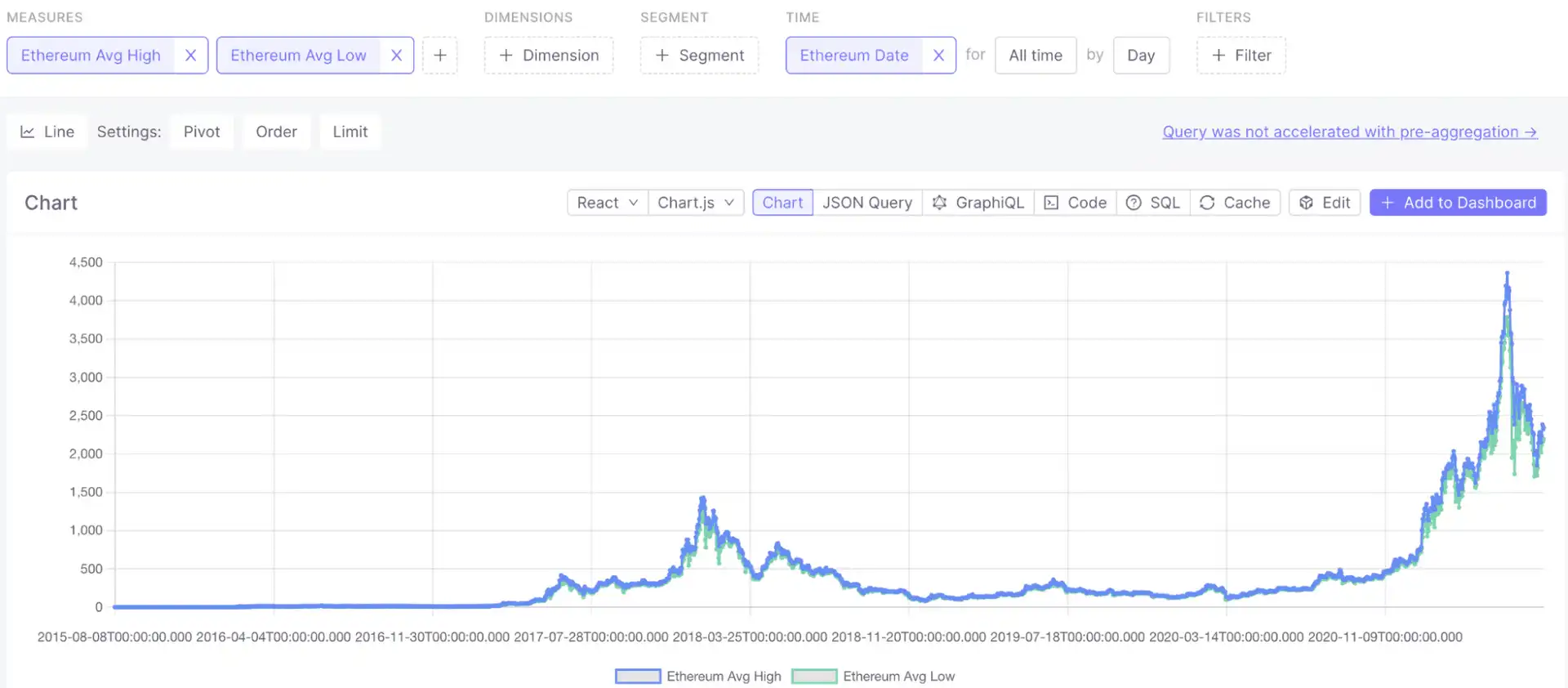
Pre-aggregations
Cube can pre-aggregate data to speed up queries. It creates materialized rollups of specified dimensions and measures, then uses aggregate awareness logic to route queries to the most optimal pre-aggregation.
Add a preAggregations block to your cube definition in Ethereum.js:
cube(`Ethereum`, {
sql: `SELECT * FROM ethereum`,
preAggregations: {
main: {
measures: [avgHigh, avgLow],
timeDimension: date,
granularity: "day"
}
},
measures: {
// ... existing measures
},
dimensions: {
// ... existing dimensions
},
})
QuestDB also supports materialized views that can be used to speed up queries directly at the database level.
Consuming Data via APIs
Cube's API-first approach enables you to connect to any data application. API endpoints ensure that metrics are consistent across different applications, tools, and teams.
Three API endpoints are available:
-
REST API: Connect your application backend via the REST API.
-
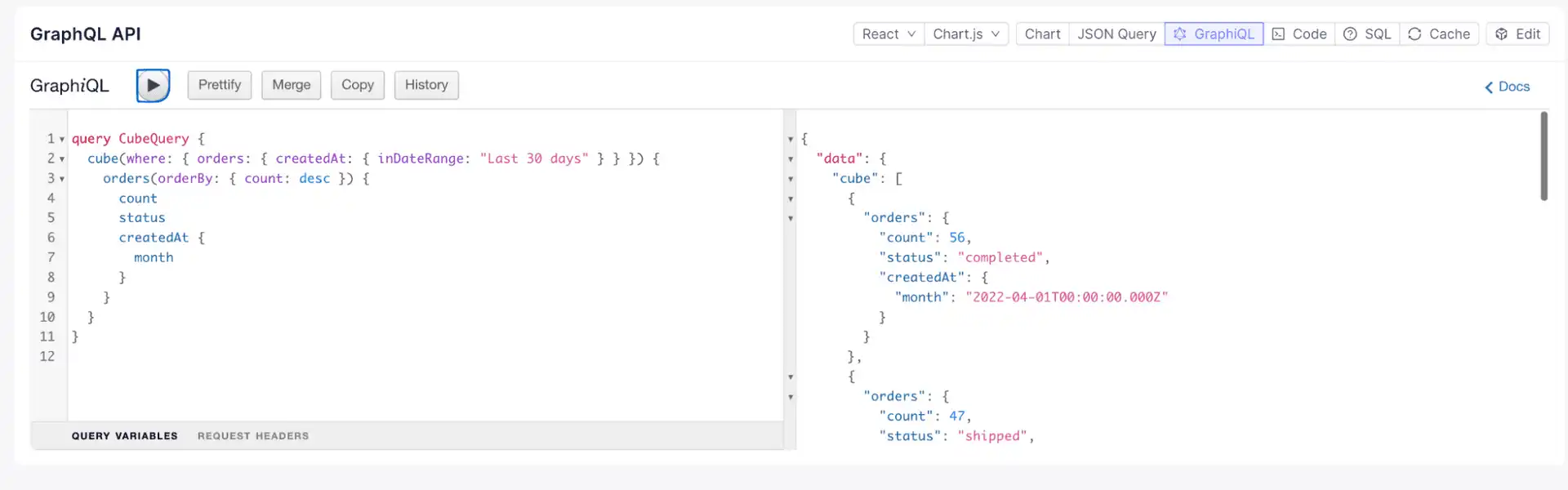
GraphQL API: Use standard GraphQL queries for embedded analytics via the GraphQL API.
-
SQL API: Query data using standard ANSI SQL via the SQL API. This is useful for BI tools, dashboards, or data science models.